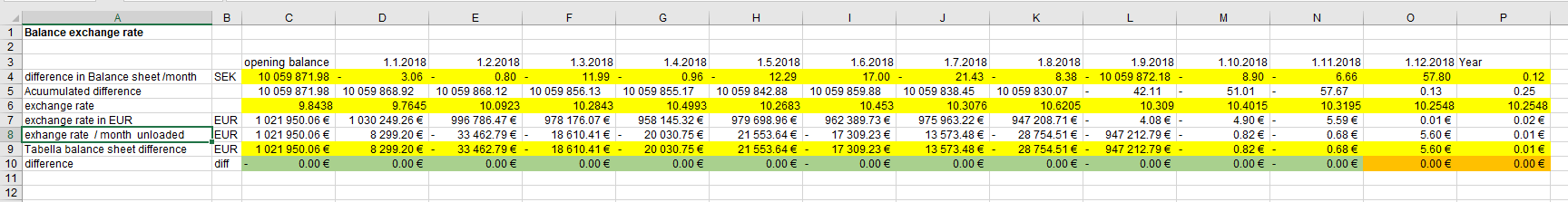
Cumulative exchange difference, table examples
Cumulative exchange difference can be take in use also with P/L accounts. It is automatically in use with balance sheet. See Maintenance of currencies.
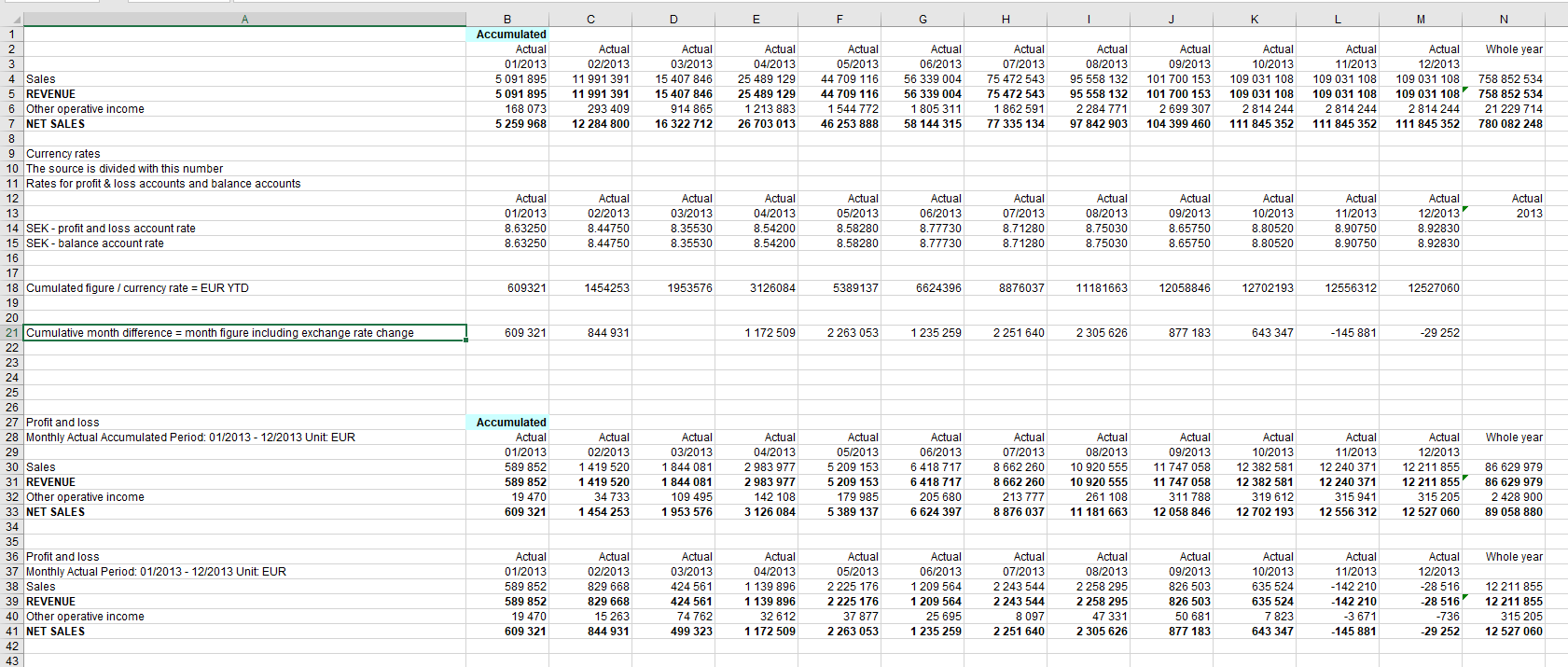
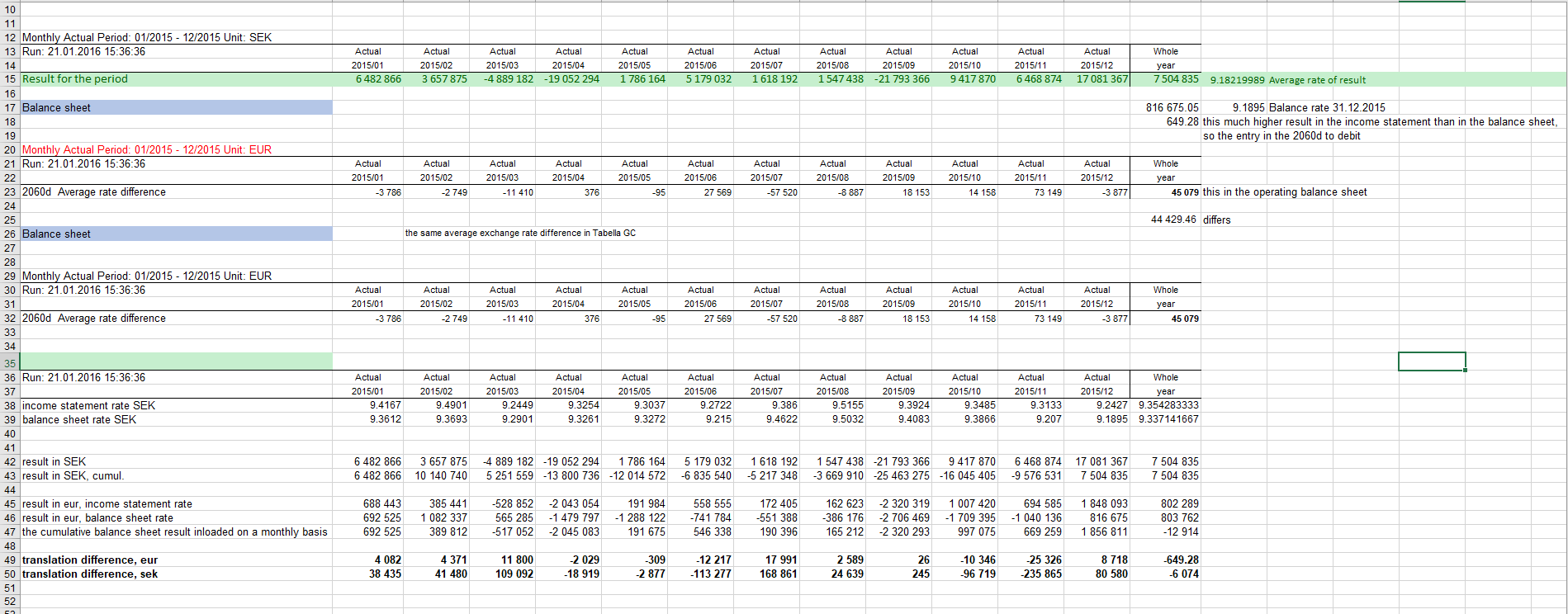
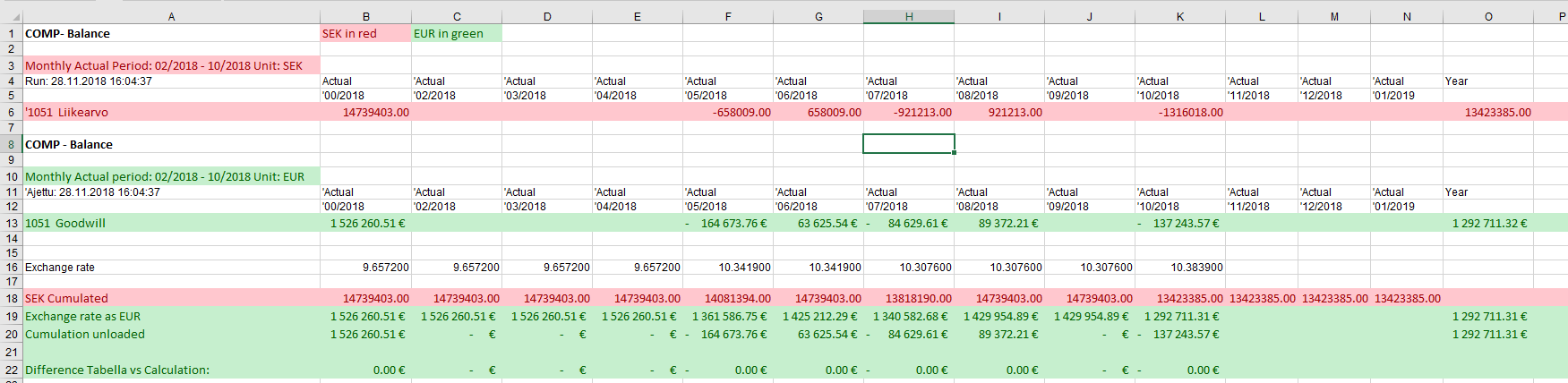
In report accumulated exchange rate is used: numbers are accumulated, exhange rate is used and then numbers are de-accumulated leaving for months, difference vs. previous month .
This means, that the month’s figure may not match the figue shown in transaction level.
In the transaction level accumulation is not done, therefore the sum may differ compared that shown in the report.
In transcations, the original currency entry is shown in its own column.
Note
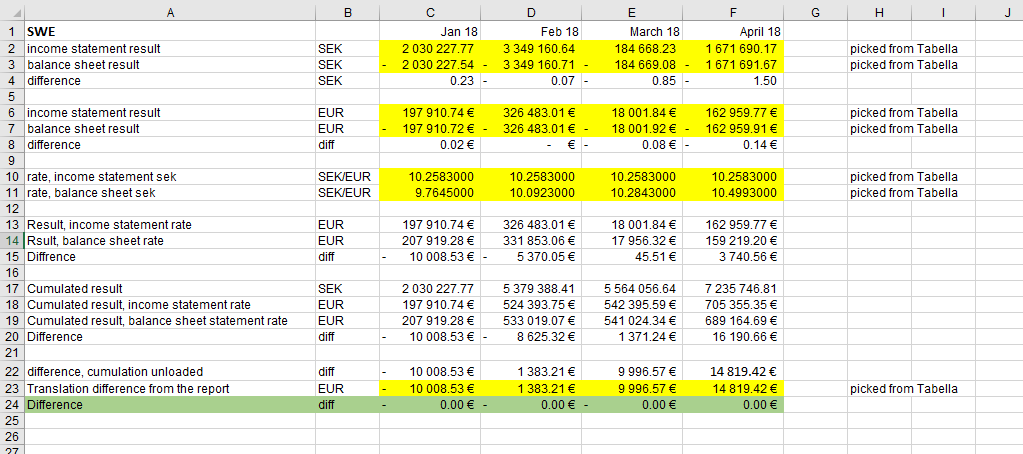
Commonly, in the consolidated financial statements of foreign companies, the year end numbers are being divided by the exchange rate dated 31.12.. Tabella will produce the same result, due to exhange accumulation, at the end of the year.
The fluctuation of the course can be seen in the months, even if there is no currency balance for the month. The fluctuation emerges also, if year-end exchange rates, for the follow-up year, are left empty. Therefore, it is recommended to fill the year-end using current month’s rate, so the end of the year is shown (€) in monthly report.
Table examples: